| HS Code | Official Doc | Tariff Rate | Origin | Destination | Effective Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7307911000 | Doc | 83.3% | CN | US | 2025-05-12 |
| 7307923010 | Doc | 80.0% | CN | US | 2025-05-12 |
| 7326908630 | Doc | 82.9% | CN | US | 2025-05-12 |
| 8113000000 | Doc | 58.7% | CN | US | 2025-05-12 |
| 7412100000 | Doc | 58.0% | CN | US | 2025-05-12 |
| 7415390000 | Doc | 58.0% | CN | US | 2025-05-12 |
| 7415338010 | Doc | 58.0% | CN | US | 2025-05-12 |
| 8305906000 | Doc | 43.2% | CN | US | 2025-05-12 |
| 8305903050 | Doc | 30.0% | CN | US | 2025-05-12 |
| 6906000000 | Doc | 55.0% | CN | US | 2025-05-12 |
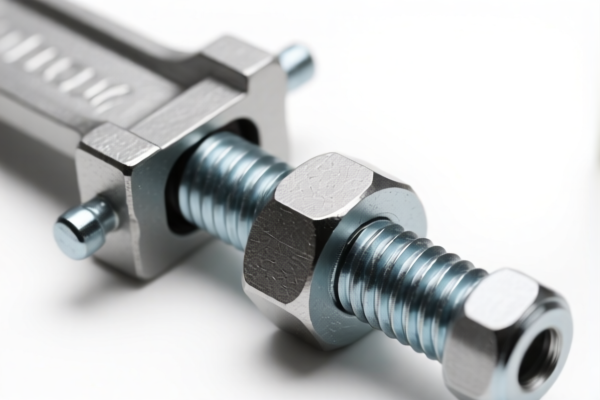



Pipe Clamp
A pipe clamp is a tool used to hold pipes and other cylindrical objects firmly in place. They are commonly employed in plumbing, woodworking, metalworking, and various construction applications.
Material
Pipe clamps are typically constructed from the following materials:
- Steel: Offers high strength and durability, suitable for heavy-duty applications. Often coated to resist corrosion.
- Cast Iron: Traditional material, known for its strength and ability to withstand significant pressure. Heavier than steel clamps.
- Aluminum: Lighter than steel, making them easier to handle, but generally less strong. Suitable for lighter-duty tasks.
- Plastic/Composite: Used in specialized clamps for applications where damage to the pipe surface is a concern, or where corrosion resistance is paramount.
Purpose
The primary purpose of a pipe clamp is to secure pipes during:
- Joining: Holding pipes together while adhesives or solvents set, or during welding or soldering.
- Assembly: Maintaining alignment during the construction of pipe systems.
- Repair: Fixing pipes in place during cutting, threading, or other repair processes.
- General Holding: Securing pipes for various tasks like painting, drilling, or modification.
Function
Pipe clamps function by applying a controlled clamping force to the pipe. The core components enable this:
- Jaws: Designed to grip the pipe without causing excessive damage. Often lined with rubber or plastic pads.
- Screw/Threaded Rod: The primary force-generating component. Rotating the rod applies pressure to the jaws.
- Handle: Provides leverage for tightening and loosening the clamp.
- Base/Frame: Provides structural support and stability.
Usage Scenarios
- Plumbing: Joining PVC, copper, or steel pipes during installation and repair.
- Woodworking: Holding pipes used as structural elements or for decorative purposes.
- Metalworking: Securing pipes during welding, cutting, or bending.
- Automotive: Holding exhaust pipes or other tubular components during repair.
- Construction: Securing pipes for scaffolding, supports, or temporary structures.
Common Types
- F-Clamp (Standard Pipe Clamp): The most common type, featuring an open "F" shape. Suitable for general-purpose applications.
- C-Clamp: Similar to F-clamps, but with a "C" shape. Often used for smaller pipes or in confined spaces.
- Quick-Release Clamp: Features a lever mechanism for rapid clamping and release. Useful for repetitive tasks.
- Spring Clamp: Uses spring pressure to hold pipes in place. Suitable for lighter-duty applications.
- Chain Clamp: Utilizes a chain to wrap around the pipe, allowing for clamping of pipes with varying diameters. Common in industrial settings.
- Roller Clamp: Features rollers to distribute pressure evenly around the pipe, minimizing the risk of damage.
- Web Clamp: Uses a strap to secure the pipe, providing a versatile clamping solution for irregular shapes.
Pipe clamps are fittings used to secure and support tubes and pipes. They are commonly employed in construction, plumbing, and industrial applications for fastening pipes to structures or other pipes. Depending on the material, they can be made of iron, steel, or other metals.
The following HS codes may be relevant:
- 7307.91.10.00: This code covers tube or pipe fittings (such as couplings, elbows, sleeves) of iron or steel, specifically 'Other' category, and further specifies 'Flanges' that are 'Not machined, not tooled and not otherwise processed after forging' and are 'Of iron or nonalloy steel'.
- 7307.92.30.10: This code also covers tube or pipe fittings of iron or steel, categorized as 'Other', and further defines 'Threaded elbows, bends and sleeves', specifically 'Sleeves (couplings)' made of 'Of iron or nonalloy steel'.
- 7326.90.86.30: This code covers 'Other articles of iron or steel', specifically 'Other', and further specifies 'Other Hangers and similar supports for tubes and pipes'. This is likely the most applicable code for pipe clamps functioning as supports.
Regarding HS code 7326.90.86.30, it is important to note that this covers hangers and supports. If the pipe clamp is functioning as a direct connector, 7307.91.10.00 or 7307.92.30.10 may be more appropriate.
It is recommended to carefully consider the function of the pipe clamp to determine the most accurate HS code.
Customer Reviews
No reviews yet.