| HS Code | Official Doc | Tariff Rate | Origin | Destination | Effective Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9027106000 | Doc | 55.0% | CN | US | 2025-05-12 |
| 9027894530 | Doc | 55.0% | CN | US | 2025-05-12 |
| 8543708000 | Doc | 55.0% | CN | US | 2025-05-12 |
| 8543906800 | Doc | 55.0% | CN | US | 2025-05-12 |
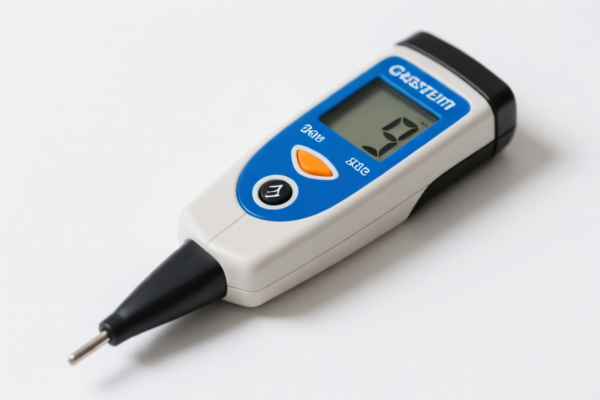
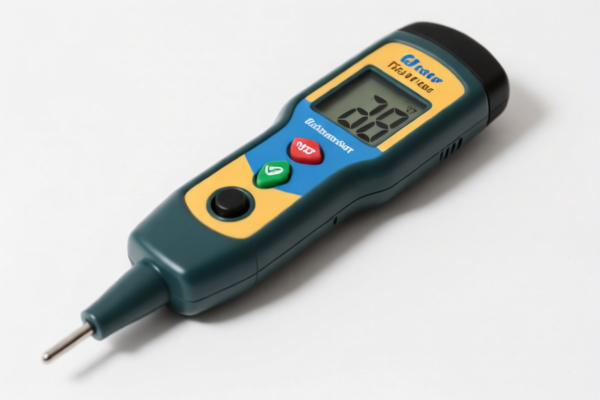
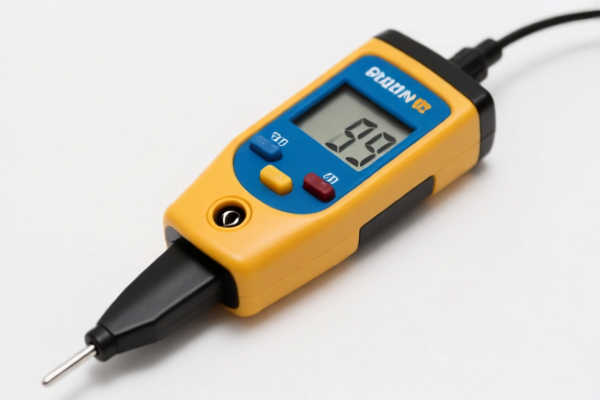
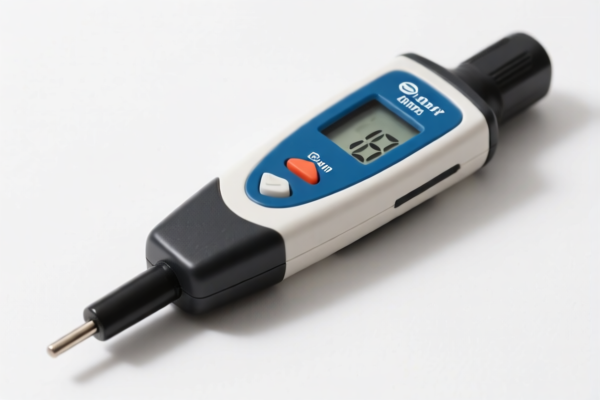



Soil pH Meter
A soil pH meter is a device used to measure the acidity or alkalinity of soil. Soil pH is a crucial factor influencing nutrient availability, plant growth, and overall soil health.
Principle of Operation:
Most soil pH meters operate using an electrochemical method. A glass electrode, sensitive to hydrogen ion activity, is inserted into the soil, along with a reference electrode. The difference in electrical potential between these electrodes is measured, which corresponds to the pH level of the soil. Some simpler meters utilize colorimetric methods, relying on chemical reactions to indicate pH through color changes.
Purpose:
- Agricultural Optimization: Determining optimal pH levels for specific crops to maximize nutrient uptake and yield.
- Gardening: Assessing soil conditions for healthy plant growth and identifying potential deficiencies.
- Environmental Monitoring: Evaluating soil quality and potential pollution impacts.
- Research: Conducting scientific studies on soil chemistry and plant physiology.
Function:
The primary function is to provide a quantitative measurement of soil pH, typically on a scale of 0 to 14.
- pH < 7: Indicates acidic soil.
- pH = 7: Indicates neutral soil.
- pH > 7: Indicates alkaline (basic) soil.
The meter displays the pH value, allowing users to adjust soil conditions as needed.
Usage Scenarios:
- Farms: Regularly monitoring pH levels in different fields to optimize fertilizer application and crop rotation.
- Home Gardens: Testing soil before planting, during the growing season, and after amendments.
- Lawns: Assessing pH for healthy grass growth.
- Greenhouses: Maintaining optimal pH levels for potted plants.
- Laboratories: Analyzing soil samples for research purposes.
Common Types:
- Analog Soil pH Meters: Traditional meters with a needle display. Require calibration and may be less accurate than digital models.
- Digital Soil pH Meters: Provide a clear digital readout, often with automatic calibration features. Generally more accurate and user-friendly.
- Pen-Type Soil pH Meters: Portable and compact, suitable for quick on-site measurements.
- In-Situ Soil pH Meters: Designed for continuous monitoring of soil pH in a specific location. Often used in research applications.
- Colorimetric Soil pH Test Kits: Utilize chemical indicators to determine pH based on color comparison. Less precise but affordable and easy to use.
Considerations:
- Calibration: Regular calibration is essential for accurate readings.
- Soil Contact: Ensure good contact between the electrode and the soil for reliable measurements.
- Soil Moisture: Some meters require a specific level of soil moisture for accurate results.
- Temperature: Temperature can affect pH readings; some meters have temperature compensation features.
- Electrode Maintenance: Proper cleaning and storage of the electrode are crucial for longevity and accuracy.
A soil pH meter is an instrument used to measure the acidity or alkalinity of soil. It falls under the category of instruments for physical or chemical analysis.
Here are the relevant HS codes based on the provided reference material:
-
9027106000: Instruments and apparatus for physical or chemical analysis (for example, polarimeters, refractometers, spectrometers, gas or smoke analysis apparatus); instruments and apparatus for measuring or checking viscosity, porosity, expansion, surface tension or the like; instruments and apparatus for measuring or checking quantities of heat, sound or light (including exposure meters); microtomes; parts and accessories thereof: Gas or smoke analysis apparatus: Other: Other. This code covers instruments for chemical analysis, which includes pH measurement.
- 90: Chapter 90 – Instruments and apparatus which measure, check, test, navigate or control.
- 27: Heading 9027 – Instruments and apparatus which measure or check the physical properties of substances or states of matter; instruments and apparatus for measuring or checking quantities of heat, sound or light.
- 10: Subheading 9027.10 – Instruments and apparatus for physical or chemical analysis.
- 60: Further breakdown specifying Gas or smoke analysis apparatus, Other, Other.
-
9027894530: Instruments and apparatus for physical or chemical analysis (for example, polarimeters, refractometers, spectrometers, gas or smoke analysis apparatus); instruments and apparatus for measuring or checking viscosity, porosity, expansion, surface tension or the like; instruments and apparatus for measuring or checking quantities of heat, sound or light (including exposure meters); microtomes; parts and accessories thereof: Other instruments and apparatus: Other: Other: Electrical Chemical analysis instruments and apparatus. This code specifically covers electrical chemical analysis instruments and apparatus, which a soil pH meter often is.
- 90: Chapter 90 – Instruments and apparatus which measure, check, test, navigate or control.
- 27: Heading 9027 – Instruments and apparatus which measure or check the physical properties of substances or states of matter; instruments and apparatus for measuring or checking quantities of heat, sound or light.
- 89: Subheading 9027.89 – Other instruments and apparatus.
- 45: Further breakdown specifying Other instruments and apparatus, Other, Other.
- 30: Further breakdown specifying Electrical Chemical analysis instruments and apparatus.
Tax Information:
Both HS codes 9027106000 and 9027894530 have the following tax details:
- Basic Tariff: 0.0%
- Additional Tariff: 25.0%
- Additional Tariff (after April 2, 2025): 30.0%
- Total Tariff: 55.0%
Customer Reviews
No reviews yet.