| HS Code | Official Doc | Tariff Rate | Origin | Destination | Effective Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8468805000 | Doc | 55.0% | CN | US | 2025-05-12 |
| 8468905000 | Doc | 55.0% | CN | US | 2025-05-12 |
| 8515902000 | Doc | 81.6% | CN | US | 2025-05-12 |
| 8515904000 | Doc | 55.0% | CN | US | 2025-05-12 |
| 8487900080 | Doc | 83.9% | CN | US | 2025-05-12 |
| 8487900040 | Doc | 58.9% | CN | US | 2025-05-12 |
| 7326110000 | Doc | 80.0% | CN | US | 2025-05-12 |
| 7326908688 | Doc | 82.9% | CN | US | 2025-05-12 |
| 8205591000 | Doc | 62.2% | CN | US | 2025-05-12 |
| 8205700060 | Doc | 60.0% | CN | US | 2025-05-12 |
| 8206000000 | Doc | The rate of duty applicable to that article in the set subject t+30.0% | CN | US | 2025-05-12 |
| 8203206030 | Doc | 12¢/doz. + 5.5%+55.0% | CN | US | 2025-05-12 |
| 8203206060 | Doc | 12¢/doz. + 5.5%+55.0% | CN | US | 2025-05-12 |
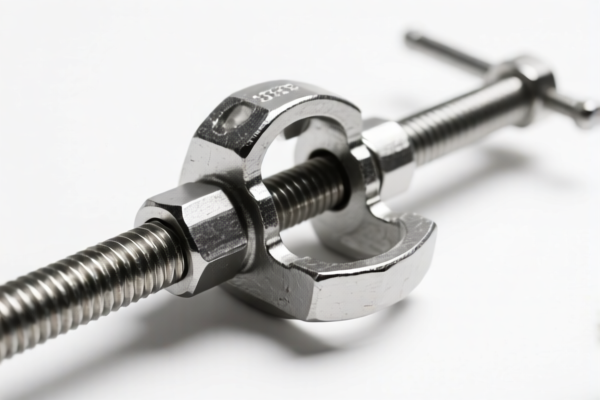
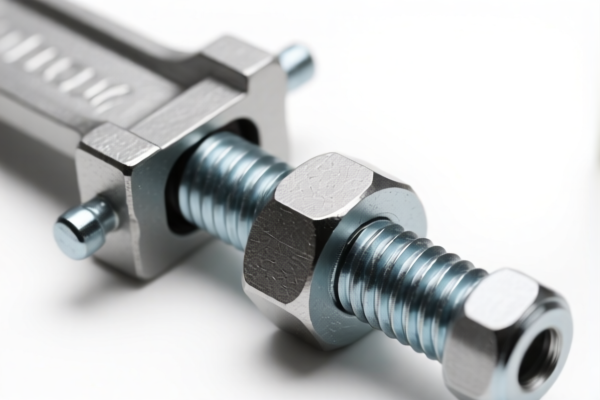



Welding Clamp
A welding clamp is a tool used to hold metal pieces together securely during the welding process. They prevent movement of the workpieces, ensuring accurate and consistent welds.
Material
Welding clamps are typically constructed from:
- Steel: Most common material due to its strength and durability. Carbon steel is frequently used.
- Stainless Steel: Used in applications requiring corrosion resistance, such as welding stainless steel or in damp environments.
- Aluminum: Lighter weight option, suitable for certain applications where steel's weight is a concern, and for welding aluminum alloys.
- Cast Iron: Found in older or heavier-duty clamps, offering significant clamping force.
Purpose
The primary purpose of a welding clamp is to:
- Secure Workpieces: Hold metal parts in the desired position.
- Maintain Alignment: Prevent shifting or distortion during welding.
- Ensure Weld Quality: Consistent positioning leads to stronger, cleaner welds.
- Increase Safety: Freeing the welder's hands for operating welding equipment.
Function
Welding clamps function by applying pressure to the workpieces, utilizing:
- Leverage: Many clamps use a lever mechanism to amplify force.
- Friction: Clamping surfaces create friction to resist movement.
- Mechanical Advantage: Designs incorporate features to increase the force applied with minimal effort.
- Adjustability: Allow for accommodating varying material thicknesses and shapes.
Usage Scenarios
Welding clamps are used in a wide variety of welding applications, including:
- Structural Welding: Construction, bridge building, and fabrication of steel structures.
- Automotive Repair: Repairing vehicle frames and body panels.
- Pipe Welding: Securing pipes during welding processes.
- Sheet Metal Fabrication: Holding thin metal sheets together for welding.
- DIY Projects: Home repairs, hobby welding, and small fabrication tasks.
Common Types
Several types of welding clamps are available, each suited for specific tasks:
- C-Clamps: Versatile, general-purpose clamps with a C-shaped frame. Available in various sizes.
- Spring Clamps: Quick-release clamps for temporary holding. Useful for tack welding.
- Vice Grips (Locking Pliers): Can function as clamps for smaller pieces or irregular shapes.
- Edge Clamps: Designed to clamp edges of metal sheets together, often used in sheet metal fabrication.
- F-Clamps: Similar to C-clamps, but with a wider opening for larger workpieces.
- Welding Pliers: Specialized pliers with features for manipulating and clamping metal.
- Chain Clamps: Used for clamping large or irregularly shaped objects.
- Magnetic Clamps: Utilize magnets to hold ferrous metal pieces together.
- Quick-Grip Clamps: Offer rapid clamping and release for efficiency.
Welding clamps are tools used to hold metal pieces securely in place during welding, brazing, or soldering processes. They are essential for ensuring accurate and safe joining of materials.
The following HS codes are relevant to welding clamps, based on the provided reference material:
- 8205.59.10.00: This HS code falls under Chapter 82: Handtools (including glass cutters) not elsewhere specified or included; blow torches and similar self-contained torches; vises, clamps and the like, other than accessories for and parts of machine tools or water-jet cutting machines; anvils; portable forges; hand- or pedal-operated grinding wheels with frameworks; base metal parts thereof. Specifically, it covers Heading 8205: Other handtools (including glass cutters) and parts thereof, and further specifies Subheading 8205.59.10.00: Other handtools (including glass cutters) and parts thereof: Other: Pipe tools, and parts thereof. This suggests that welding clamps used for pipe welding may fall under this code. The total tax rate is 62.2%.
- 8205.70.00.60: This HS code also falls under Chapter 82: Handtools (including glass cutters) not elsewhere specified or included; blow torches and similar self-contained torches; vises, clamps and the like, other than accessories for and parts of machine tools or water-jet cutting machines; anvils; portable forges; hand- or pedal-operated grinding wheels with frameworks; base metal parts thereof. Specifically, it covers Heading 8205: Vises, clamps and the like, and parts thereof, and further specifies Subheading 8205.70.00.60: Vises: Other. This code is applicable to general-purpose welding clamps that function as vises. The total tax rate is 60.0%.
- 8468.80.50.00: This HS code falls under Chapter 84: Machinery and apparatus for soldering, brazing or welding, whether or not capable of cutting, other than those of heading 8515; gas-operated surface tempering machines and appliances; parts thereof. Specifically, it covers Heading 8468: Other machinery and apparatus. This code may be applicable if the welding clamp is part of a larger welding apparatus. The total tax rate is 55.0%.
Regarding HS code 8205.59.10.00 and 8205.70.00.60, please note that these codes cover handtools. If the welding clamp is a component of a larger machine, HS code 8468.80.50.00 may be more appropriate.
Customer Reviews
No reviews yet.