| HS Code | Official Doc | Tariff Rate | Origin | Destination | Effective Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8307103000 | Doc | 58.8% | CN | US | 2025-05-12 |
| 8307903000 | Doc | 58.8% | CN | US | 2025-05-12 |
| 8308909000 | Doc | 57.7% | CN | US | 2025-05-12 |
| 8503009580 | Doc | 58.0% | CN | US | 2025-05-12 |
| 8503009520 | Doc | 83.0% | CN | US | 2025-05-12 |
| 8548000000 | Doc | 55.0% | CN | US | 2025-05-12 |
| 8479899599 | Doc | 57.5% | CN | US | 2025-05-12 |
| 8485909000 | Doc | 55.0% | CN | US | 2025-05-12 |
| 8485800000 | Doc | 57.5% | CN | US | 2025-05-12 |
| 7312900000 | Doc | 80.0% | CN | US | 2025-05-12 |
| 7312100500 | Doc | 80.0% | CN | US | 2025-05-12 |
| 7326200090 | Doc | 83.9% | CN | US | 2025-05-12 |
| 7326908688 | Doc | 82.9% | CN | US | 2025-05-12 |
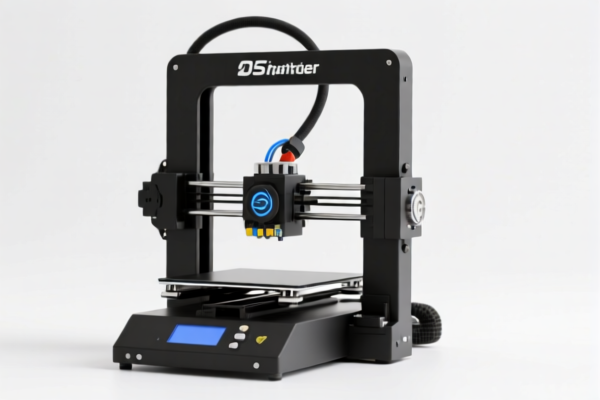
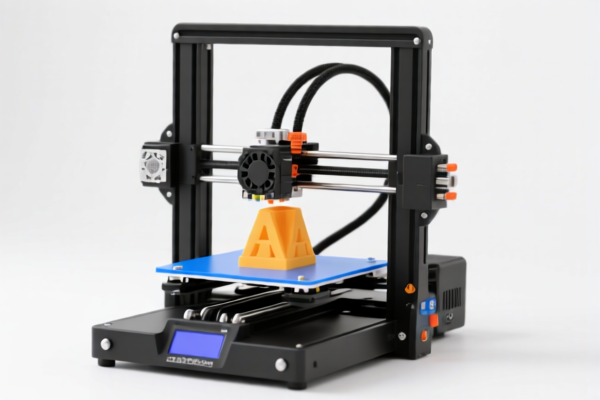

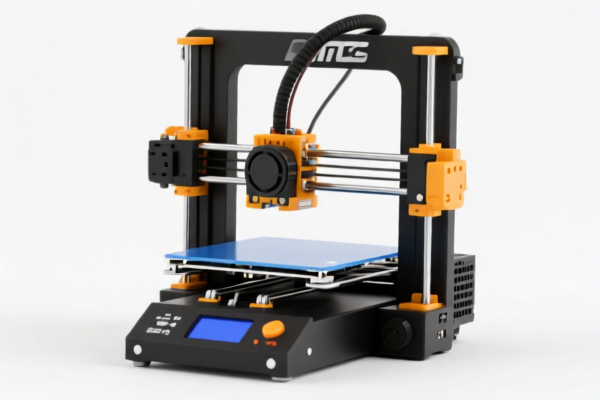
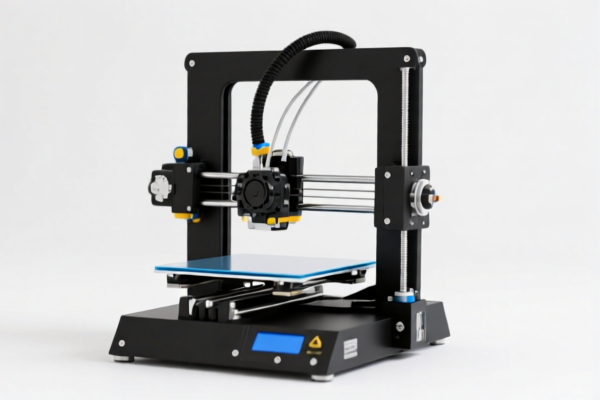
3D Printer Drag Chain
A drag chain, also known as a cable carrier, energy chain, or cable track, is a guiding component used in 3D printers to manage and protect electrical cables and hoses as they move along multiple axes. It prevents tangling, wear, and potential damage to these essential components during printer operation.
Material
Drag chains are commonly manufactured from several materials, each offering different properties:
- Plastic (Nylon, HDPE, PP): Lightweight, cost-effective, and suitable for most indoor 3D printer applications. Often used for smaller printers or less demanding environments.
- Steel: Offers higher strength and durability, making them ideal for larger printers, industrial applications, or environments with higher temperatures or stresses. May be coated for corrosion resistance.
- Hybrid (Steel/Plastic): Combines the strength of steel with the cost-effectiveness and noise-dampening properties of plastic.
Purpose
The primary purpose of a drag chain is to:
- Protect Cables & Hoses: Shield delicate cables and hoses from abrasion, crushing, and other physical damage.
- Prevent Tangling: Organize and guide cables, preventing them from becoming tangled or snagged during movement.
- Extend Cable Lifespan: Reduce wear and tear, prolonging the life of cables and hoses.
- Reduce Noise: Minimize friction and noise generated by cables rubbing against printer components.
- Maintain Cable Organization: Provides a clean and structured appearance to the printer's wiring.
Function
Drag chains function by housing cables and hoses within interconnected links. These links are designed to bend and flex in multiple directions, allowing the cables to move freely along the printer's axes without becoming strained or damaged. The chain is supported by rollers or sliders, depending on the design, to reduce friction and ensure smooth movement.
Usage Scenarios
- CoreXY Printers: Essential for managing the cables of the stepper motors and endstops in CoreXY designs, where cables travel significant distances.
- Delta Printers: Used to organize and protect cables as they move along the arms of the delta printer.
- Cartesian Printers: Commonly found on Cartesian printers to guide cables along the X, Y, and Z axes.
- Large Format Printers: Crucial for managing the extensive cabling required for larger printers.
- Industrial 3D Printers: Often employed in industrial settings where durability and reliability are paramount.
Common Types
- Open Type: Features open links, allowing for easy access to cables for inspection or replacement. More affordable but offers less protection.
- Closed Type: Encloses cables completely within closed links, providing greater protection against dust, debris, and physical damage.
- Floating Type: Designed for applications where cables are subject to high bending radii or complex movements. Offers greater flexibility and durability.
- Micro Chain: Smaller drag chains designed for compact 3D printers or robotics applications.
- Heavy Duty Chain: Robust drag chains made from steel or hybrid materials for industrial applications.
- Chain with Integrated Rollers/Sliders: Some drag chains incorporate rollers or sliders directly into the links to reduce friction and ensure smooth movement.
Based on the provided information, a “3d printer drag chain” can be classified under the following HS codes:
- 8479899599: Machines and mechanical appliances having individual functions, not specified or included elsewhere in this chapter; parts thereof: Other machines and mechanical appliances: Other: Other Other. This code covers parts of other machines and mechanical appliances. A drag chain used as a component of a 3D printer could fall under this classification. The total tax rate is 57.5%.
- 8503009580: Parts suitable for use solely or principally with the machines of heading 8501 or 8502: Other: Other Other: Other. If the drag chain is specifically designed as a part for machines heading 8501 or 8502, this code may apply. The total tax rate is 58.0%.
- 7326200090: Other articles of iron or steel: Articles of iron or steel wire Other. If the drag chain is made of iron or steel wire, this code is applicable. The total tax rate is 83.9%.
- 7326908688: Other articles of iron or steel: Other: Other: Other: Other Other. This code covers other articles of iron or steel. The total tax rate is 82.9%.
Important Considerations:
Regarding HS codes 7326200090 and 7326908688, please note the need to verify the material as steel and may require verification of the composition. Additionally, for HS codes 7326200090 and 7326908688, a 25% additional tariff applies to steel and aluminum products.
Customer Reviews
The detailed information on the purpose and function of drag chains was exactly what I needed to understand their importance in 3D printers. Highly recommended.
I appreciate the breakdown of the different materials used in drag chains and how they affect the HS code classification. Very informative.
The page provided a clear breakdown of the different HS codes and their corresponding tariff rates. This helped me make an informed decision for my export.
I was looking for HS codes for steel drag chains and found the relevant ones. The note about the 25% additional tariff was really useful.
The detailed explanation of the 8503009580 code made it easy to understand how my drag chain fits into the classification system. Great resource!